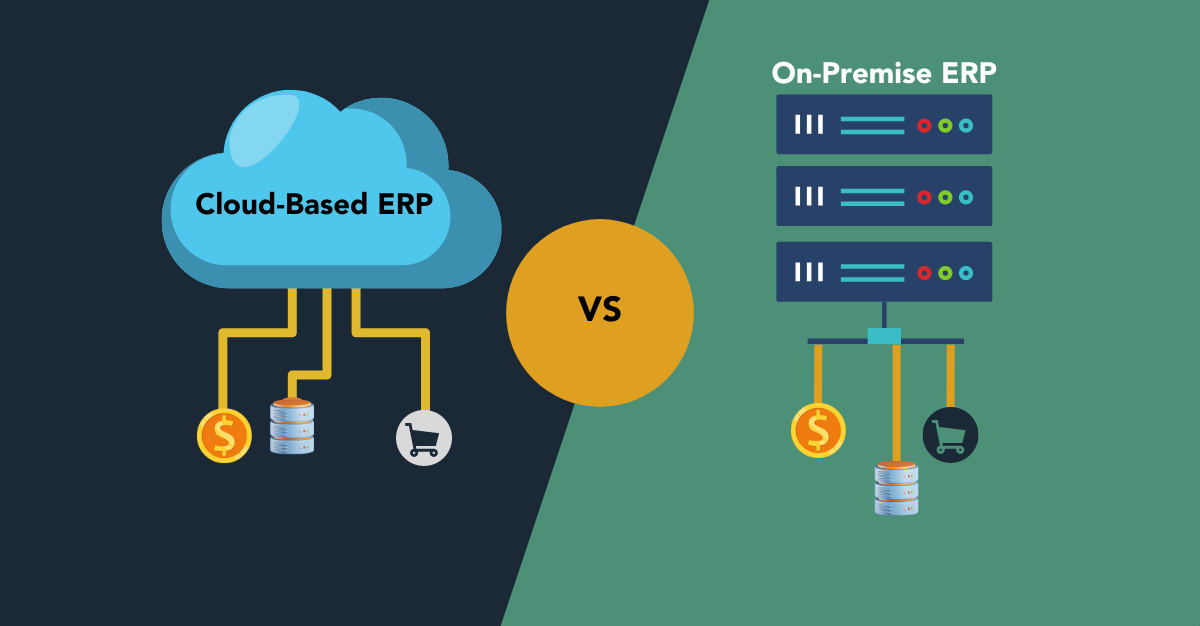
In the world of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, one of the most important decisions businesses face is whether to implement a Cloud ERP or an On-Premises ERP. Both options have their advantages and drawbacks, and the choice depends on factors such as business size, industry, budget, and specific operational needs. Here, we’ll explore the key differences, pros, and cons of each solution to help you make an informed decision.
What is Cloud ERP?
Cloud ERP is hosted on a vendor’s servers and accessed via the internet. Businesses pay a subscription fee to use the software, which is maintained and updated by the provider. Cloud ERP is often referred to as “Software as a Service (SaaS).”
What is On-Premises ERP?
On-Premises ERP is installed locally on a company’s own servers and hardware. The business owns the software license and is responsible for managing and maintaining the system.
Pros and Cons of Cloud ERP
Pros
1. Lower Initial Costs
Cloud ERP operates on a subscription-based model, making it more affordable upfront. There’s no need to invest in expensive hardware or infrastructure.
2. Faster Implementation
With no physical setup required, cloud ERP systems can be deployed much quicker compared to on-premises solutions.
3. Scalability
Cloud ERP systems can easily scale up or down as your business grows, accommodating additional users, locations, or features without significant disruption.
4. Accessibility
Users can access the system anytime, anywhere, as long as they have an internet connection. This is particularly beneficial for remote or global teams.
5. Automatic Updates
The vendor manages updates and upgrades, ensuring that the system always runs the latest features and security patches.
6. Enhanced Security
Leading vendors invest heavily in data security, often offering protections that small and medium-sized businesses may not afford on their own.
Cons
1. Recurring Costs
While the upfront cost is lower, subscription fees can add up over time, potentially making cloud ERP more expensive in the long run.
2. Dependence on Internet Connectivity
Cloud ERP requires a reliable internet connection. Downtime or slow internet can disrupt operations.
3. Limited Customization
Most cloud ERPs are designed to serve a broad audience, which can make deep customizations challenging.
4. Data Control
Data is stored on the vendor’s servers, which can raise concerns about data ownership and privacy.
Pros and Cons of On-Premises ERP
Pros
1. Full Control Over Data
Businesses have complete ownership and control of their data, which is stored locally.
2. Customization
On-premises ERP systems allow for greater customization to meet specific business needs.
3. No Recurring Subscription Costs
After the initial investment, ongoing costs are limited to maintenance and support, which can be more predictable.
4. Operates Without Internet
On-premises ERP does not rely on internet connectivity, making it suitable for businesses in areas with unreliable internet.
Cons
1. High Upfront Costs
The initial cost of purchasing software licenses, servers, and other infrastructure is significant.
2. Longer Implementation Time
Setting up hardware and customizing the system can take months or even years.
3. Maintenance Responsibility
Businesses are responsible for system maintenance, updates, and security. This often requires an in-house IT team or external consultants.
4. Limited Scalability
Expanding an on-premises system can be costly and time-consuming, especially if additional hardware is required.
5. Risk of Obsolescence
Technology evolves rapidly, and businesses may find their on-premises ERP system outdated if upgrades are not regularly performed.
Which ERP is Right for Your Business?
The choice between Cloud ERP and On-Premises ERP depends on your business’s unique needs. Consider the following:
1. Budget: If upfront costs are a concern, Cloud ERP is typically the better choice.
2. Customization Needs: If your business requires extensive customization, On-Premises ERP might be more suitable.
3. Scalability: For rapidly growing businesses, Cloud ERP offers the flexibility to scale without significant investment.
4. Data Control: If regulatory or privacy concerns are critical, On-Premises ERP provides more control over data.
5. IT Resources: If your business lacks a robust IT team, Cloud ERP can alleviate the burden of maintenance and support.
6. Geography: If your team is remote or global, Cloud ERP’s accessibility may be essential.
Conclusion
Both Cloud ERP and On-Premises ERP have their strengths and weaknesses. For businesses seeking flexibility, cost-efficiency, and fast deployment, Cloud ERP is often the ideal choice. On the other hand, companies that prioritize data control and extensive customization may prefer On-Premises ERP. By evaluating your business’s goals, budget, and operational needs, you can select the ERP solution that drives efficiency and growth.